Frequently Asked Questions
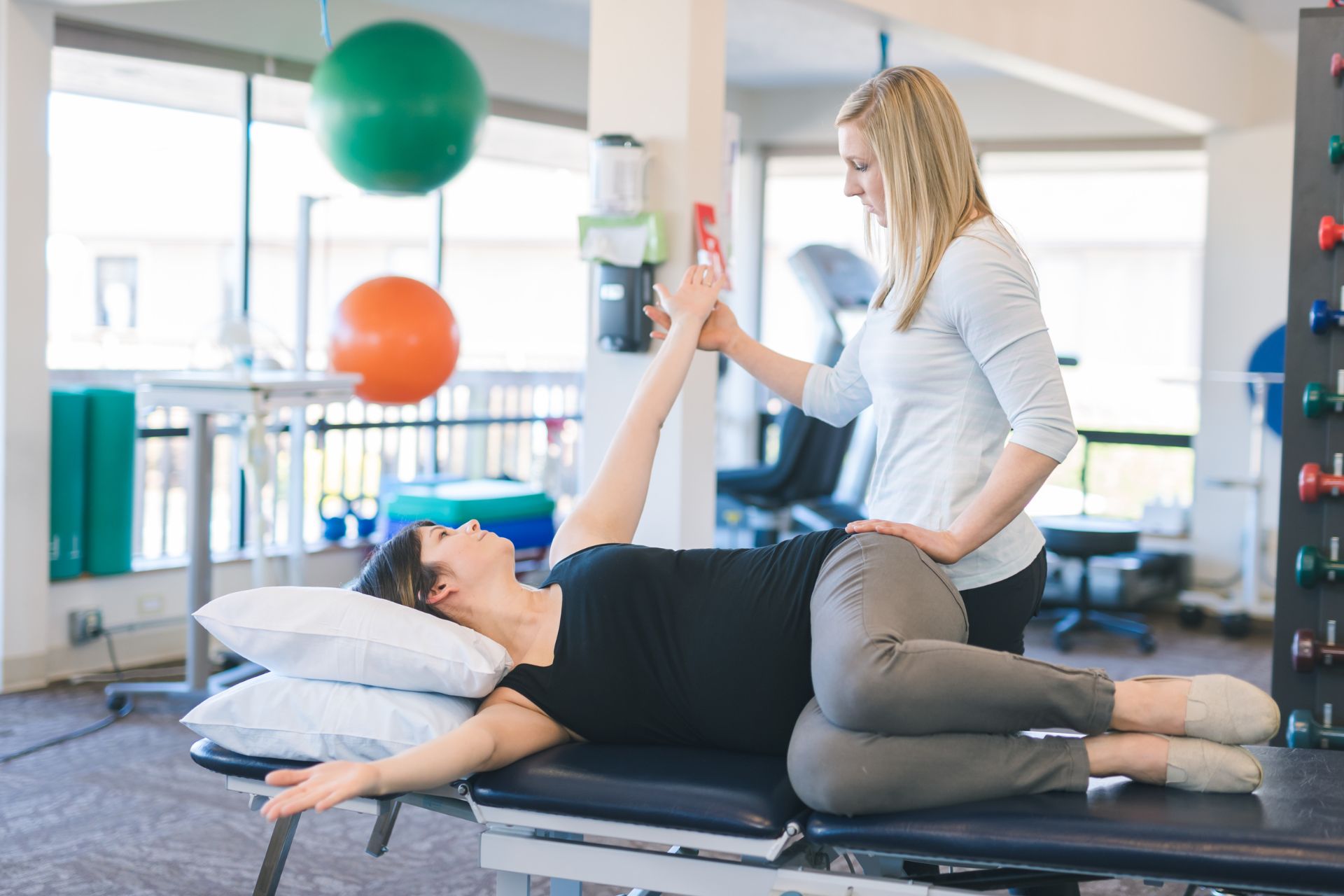
Neuromuscular reeducation employs a variety of specific techniques to address balance deficits in patients with vestibular disorders, focusing on improving proprioception, postural control, and sensory integration. Techniques such as gaze stabilization exercises enhance visual-vestibular coordination by training the oculomotor system to maintain focus during head movements. Additionally, dynamic balance activities like tandem walking or single-leg stance challenges promote stability while engaging both static and dynamic equilibrium mechanisms. Incorporating strength training for core musculature further supports postural alignment and mitigates compensatory strategies commonly observed in individuals experiencing dizziness or instability. Furthermore, the use of foam surfaces and unstable platforms introduces an element of perturbation that stimulates adaptive responses from the neuromuscular system. Vestibular rehabilitation therapy (VRT) often includes habituation exercises designed to desensitize patients to provocative stimuli inherent in daily environments while reinforcing their ability to respond effectively under varying conditions—ultimately enhancing functional mobility through targeted neuromotor pathways.
Neuromuscular reeducation in post-surgical rehabilitation focuses on restoring function and coordination after surgical interventions, emphasizing proprioceptive training, muscle activation patterns, and functional movement retraining to enhance neuromotor control. This process often involves progressive resistance exercises tailored to the specific surgical site while addressing scar tissue management and joint stability through targeted mobilizations. In contrast, acute injury management prioritizes immediate pain relief, edema control, and inflammation reduction using modalities such as cryotherapy or electrical stimulation before gradually introducing neuromuscular facilitation techniques aimed at preventing disuse atrophy. Acute protocols emphasize rapid recovery strategies that promote early range of motion activities to minimize compensatory movements leading to long-term dysfunctions. The different objectives reflect their unique contexts: optimizing healing environments post-operation versus quickly regaining mobility following an unexpected trauma.
Neuromuscular reeducation can be seamlessly integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan for patients experiencing chronic pain syndromes by employing targeted therapeutic exercises that focus on proprioceptive awareness, muscle activation patterns, and functional movement retraining. Such an approach may include techniques like neuromuscular facilitation to enhance motor control and coordination while addressing specific impairments related to postural alignment and joint stability. Additionally, incorporating biofeedback mechanisms can assist in reinforcing proper muscle engagement during rehabilitation sessions, fostering improved neuromuscular connectivity. By utilizing modalities such as electrical stimulation or manual therapy alongside progressive resistance training, healthcare providers can effectively reduce pain perception through the modulation of central sensitization pathways. Ultimately, this multidisciplinary strategy aims not only at alleviating symptoms but also at restoring optimal physiological function and enhancing the overall quality of life for individuals suffering from persistent musculoskeletal discomfort.
Proprioceptive training is a critical component of neuromuscular reeducation, particularly for athletes undergoing rehabilitation from injuries. By enhancing the awareness of body positioning and movement through targeted exercises, proprioceptive training fosters improved balance, coordination, and stability. This specialized approach employs various modalities such as balance boards, unstable surfaces like Bosu balls or foam pads, and dynamic movements to stimulate sensory feedback loops between muscles and the central nervous system. Through consistent practice, athletes can enhance joint kinesthesia and muscular control while reducing the risk of reinjury by retraining their body's neuromuscular pathways. Furthermore, effective proprioception not only aids in restoring functional movement patterns but also contributes to overall athletic performance by optimizing reaction times and agility during competitive scenarios.
Virtual reality technology significantly enhances the effectiveness of neuromuscular reeducation exercises in physical therapy settings by providing immersive and interactive environments that facilitate motor learning, proprioception, and cognitive engagement. By creating simulated scenarios tailored to individual rehabilitation needs, virtual reality can improve patients' balance, coordination, and muscle strength while simultaneously reducing anxiety associated with traditional therapeutic approaches. The use of real-time feedback on performance metrics allows therapists to monitor progress precisely and adjust treatment protocols dynamically. Furthermore, gamification elements intrinsic to virtual reality applications foster motivation and adherence among patients undergoing repetitive tasks essential for neural plasticity development. As a result, this innovative approach not only accelerates recovery times but also optimizes overall functional outcomes in movement patterns critical for daily living activities.